By James D. Roumeliotis













How often do we hear of CEOs who have been discharged for lack of performance? Contrast this with those whose Boards have kept them on the job despite controversy and/or inept leadership. The latter decision seems troubling. Consider Steve Ballmer of Microsoft and Mike Duke of Walmart amongst others.
It is my belief that the key issue here is organizational structure. Far too often, successful groups grow and get out of control. No organization should be too large. When it grows in size, inevitably it becomes overburdened and self-protecting. Incompetence is a guaranteed result.
The prime decision maker of the organization exercises a variety of leadership styles. Leadership is linked to personality. ‒ there is the empty, well compensated, well-tailored, neat and polite dapper boss; the absolutely lost and ineffective one; the barking, intimidating, eager for respect boss; then you have the hypocritical and/or bipolar type ‒ one day treats you well, whereas, the next day treats you with utter disrespect. For the most part, there is the worship me and exceedingly charismatic kind in vast numbers who mostly got there because of that particular trait along with shrewd politicking each step on the way up.
What most, as described above, do have in common is incompetence. Despite all the act and ego stroking, in the end, they do what it takes to remain in their dynamic position.
Short term results at the expense of long term consequences
Shareholders and the Boards focus on quarterly earnings growth results. As a result, we often witness severely dysfunctional decision making with public corporate leadership. This includes irresponsible behavior, as well as lack of depth and vision. HP’s Board is a case in point. It has been notoriously dysfunctional in the ways it has governed itself which resulted in a spate of upheavals over the last few years.
There is tremendous pressure to perform in a short period of time. There are no silver bullets for quick results. Seeds need to be planted for the future and for the good of the organization. Panacea creates decision making blunders which abound. At times it’s error in judgment and neglect. Every business sector is riddled with poor senior management. Here is a sample of some companies whose inept and/or negligent decision making have made headlines in unflattering ways.
– KODAK: In 1975, engineers at the company introduced the first digital camera to its executives. Rather than embracing it, fearing it would cannibalize its lucrative film sector, the top brass asked that the digital camera be kept under wraps indefinitely.
– WALMART: The company leadership has a long record of unethical behavior, from brutally exploiting workers to discriminating against women to bribing Mexican officials.
– MICROSOFT: Its CEO has remained long enough in his position to wipe out shareholder value by falling asleep at the wheel rather than vigorously pursuing web and mobile based businesses which companies such as Google and Apple, amongst others, have remained ahead of the game.
– JOHNSON & JOHNSON: Its former CEO who was employed at the company for 40 years resigned amid a series of missteps over the last few years of his tenure which damaged his and his company’s once sterling reputations. This included recalls of numerous over-the-counter well established drugs, including the largest recall of children’s non-prescription drugs, as well as medical devices. In addition, it was warned by the FDA about false claims it issued about its popular mouthwash, while another U.S. Federal agency, the Securities and Exchange Commission, charged the company with bribing doctors in several countries to prescribe its drugs and medical devices.
– ABERCROMBIE & FITCH: CEO Michael Jeffries’s snarl and insensitive remark that the brand’s apparel are solely targeted to the hip, slim, attractive and affluent “All American” teenager, offended many. As expected, it set off a storm of controversy. For someone concerned about his company’s image, the self-inflicted incident has damaged his and his company’s reputation. Even A&F’s investors are not pleased with the discriminatory statement which has negatively affected revenues and the stock price.
Organizational leadership is bestowed with the authority and accountability for creating value for customers, employees and its owners or shareholders. In spite of this, a significant weakness in running an organization is pushing for short-term profitability at the expense of solid planning. It’s my notion that the leader of many large multinational corporations, competence is not the primary value but rather the connections, politics, and clever tactics. Such “benefits” can usually compensate for incompetence.
The best-managed companies are constant achievers in their respective industries. They exude managerial excellence and financial performance is a reflection of capable management.
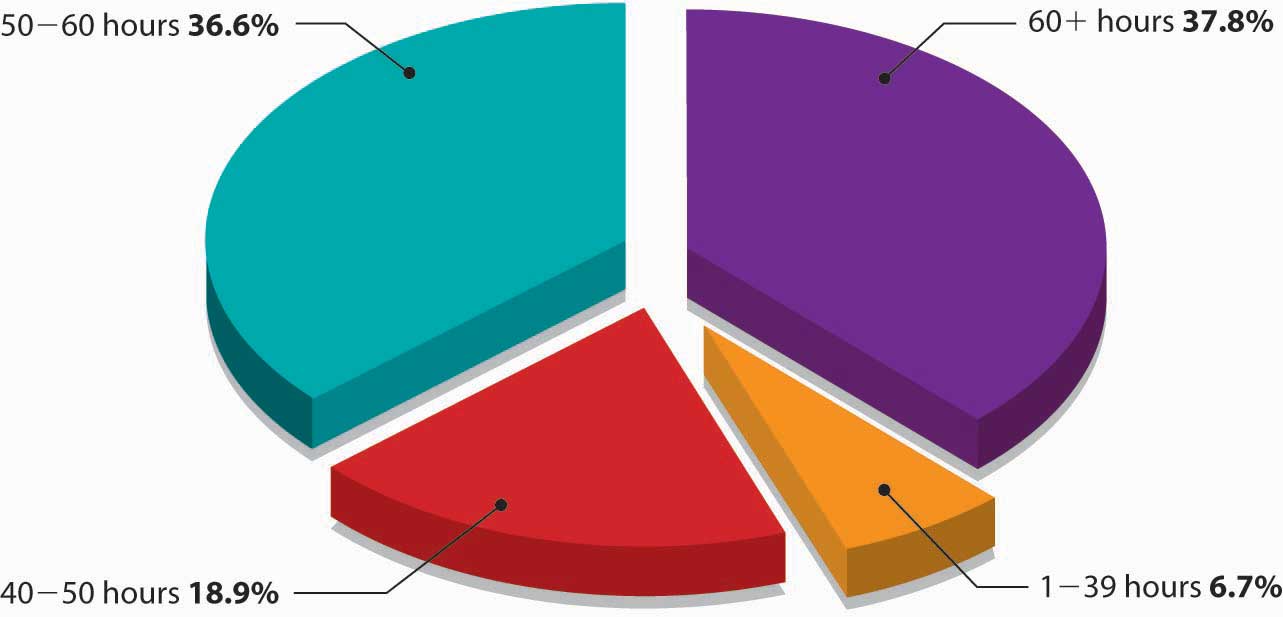
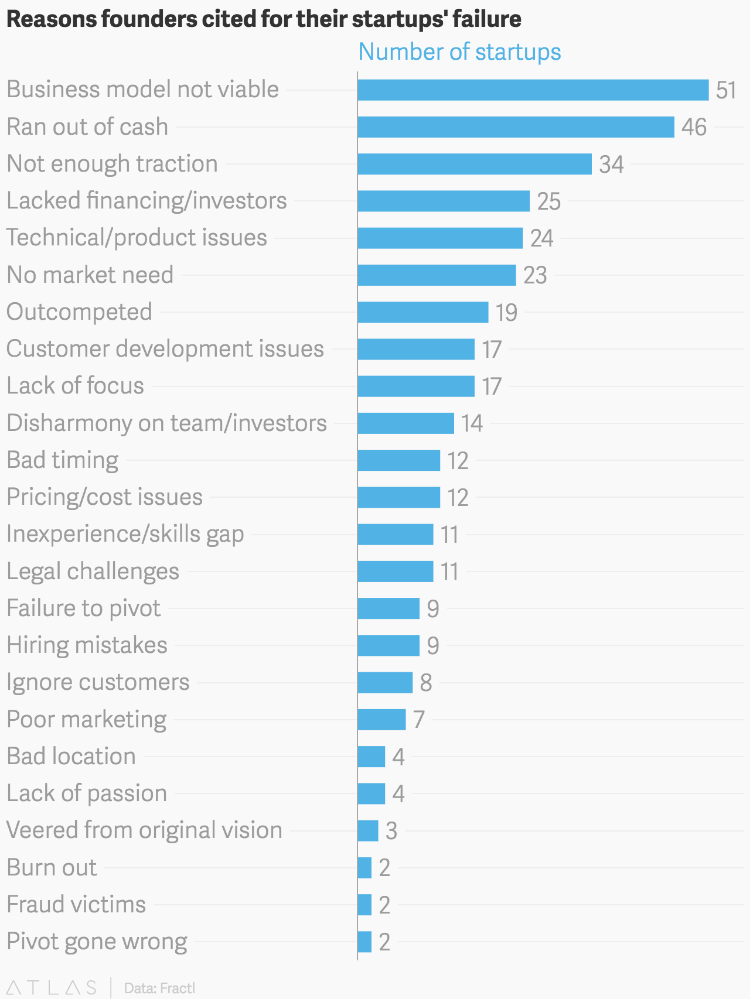
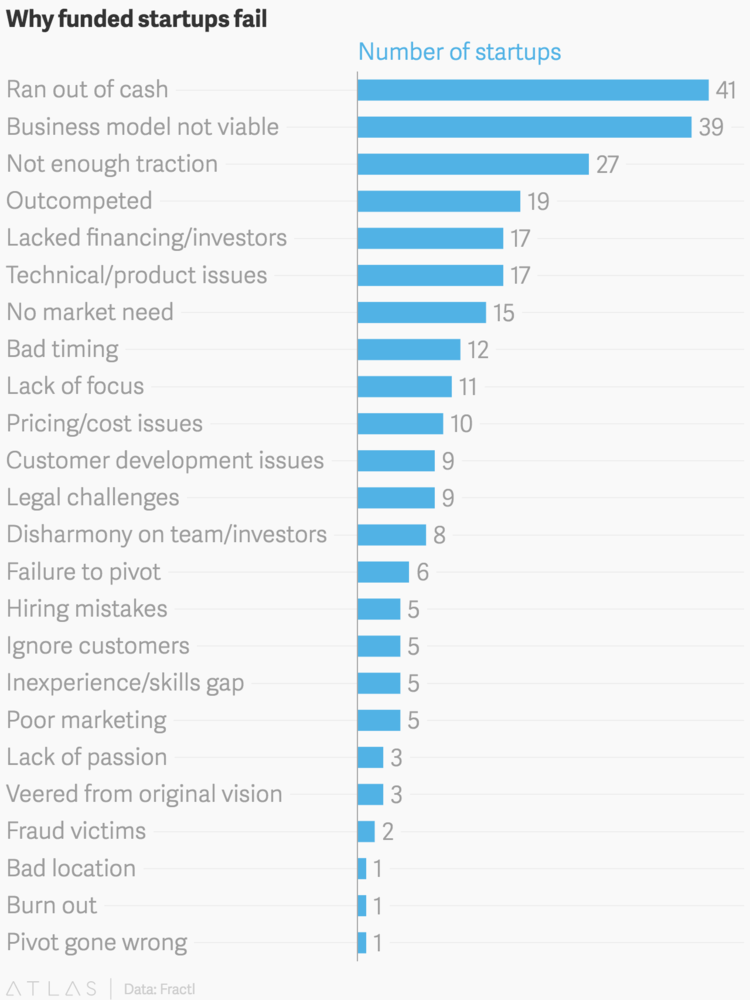
Typically, small businesses with inept ownership usually fail in the first year or two, but even companies in their growth stage can stumble badly when they outgrow the capabilities of the founding team. Research by the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics demonstrates that nearly 6 out of 10 businesses shut down within the first 4 years of operation.
Enterprises spanning a wide array of industries, have earned distinction as “well-” or “best-” managed” by demonstrating business excellence through a meticulous and independent process that evaluates their management abilities and practices – by focusing on innovation, continuous training, brainstorming and caring for their employees’ well-being – as well as investing in meeting the needs of their clients.

Identifying the shortcomings of incompetents
Regrettably, there are not many business leaders who make the cut. This includes those who also possess credentials from Ivy League educational institutions and/or oodles of charisma. A President or CEO grooming school doesn’t presently exist. Contrary to what many may think, there are no natural born leaders. In the past two decades, the average tenure of a CEO has halved. This is adequate proof how demanding the job is.
Our experiences and conditions shape who we are as people and as leaders. Leadership, like management, is not a science but a practice. The difference between the two, according to the late management guru Peter Drucker, is “Management is doing things right; leadership is doing the right things.”
Telltale signs of poor leadership in an organization include:
- in a state of denial about shortcomings – persisting with a dysfunctional status quo;
- slow/delayed decision-making process;
- lack of foresight for innovation;
- short-term selfish driven decisions with no regard for long-term consequences;
- no clear vision/strategy;
- unethical practices including apathy and lack of scruples;
- irrational thinking/decision making;
- an absence of or very little communication amongst staff and management. Chaos reigns amongst various internal departments which don’t function as a team;
- shielded from the lower ranking staff and the customer as he/she spends most, if not all of the time, behind the desk and perpetual committee meetings;
- lack of transparency ‒ there is hardly any openness from management.
Anatomy of a competent boss: in search of sustainable leadership
A prime responsibility of leadership is the capability to constantly be one step ahead of their game, to envision what lies ahead, and in the process, be well prepared to lead the organization to great heights.
Effective leaders focus on long-term growth not short term decisions to increase or stabilize the company’s stock price. Furthermore, they should be open to ideas from lower level management not exclusively from their inner circle of “yes” men/women.
The following skills may appear as a list intended for a job description. However, they should be deemed a prerequisite for a leadership role regardless of the size or type of organization.
– Bonds emotionally
– Communicates well
– Possesses character
– Accountability
– Humility, not ego
– Foresight but with an open mind for feedback
– Passionate
– Can handle criticism
– Tenacious
– Articulate
– Regard for people
– Able and willing to delegate
– Team player
– Sales and marketing savvy
– A disciplined and flexible individual who is not only open to change but a driver of change
Examples of highly effective business leaders who possess many of the above characteristics include Sir Richard Branson (Virgin Group), Megg Whitman (HP), Howard Schultz (Starbucks), Jeff Bezos (Amazon), Brad Smith (Intuit), Indra Nooyi (Pepsi), and Carlos Ghosn (Nissan), amongst others.
Public vs Private leadership ‒ and the authentic luxury enterprise
There is no doubt that the pressures and priorities of heading a private company differ as opposed to a publicly traded company. Different industry sectors may also require certain competencies.
Kellie McSorley, founder of SILK Search, the London-based boutique headhunting firm specialising in senior executive appointments in the luxury industry, explains the differences with the type of top executives sought in various sectors this way:
“For example, our Private Equity clients look for certain qualities in a person generally around urgency and result orientation whereas a Public company may place more value on other characteristics and competencies such as process, procedure and thought leadership. With Private companies there is a level of sensitivity and emotional attachment to the brand that any new hire absolutely has to understand, respect and harness, in order to succeed.”
Authentic luxury brands, on the other hand, operate by their own distinct rules as they do what it takes to retain their aura of exclusivity and cachet by focusing on production limits, premium quality and catering to UHNW patrons ‒ the antithesis of mainstream brands and products. For instance, Hermès has no need to deal with pressures of shareholders and stock analysts that are prevalent with corporate brands such as the LVMH luxury group. Instead, Hermès’ family stakeholders choose to keep the current business ethos along with their complete independence.
As for what the luxury sector desires in its future CEO, Ms. McSorley states this succinctly as follows:
“Historically C-Suite recruitment in Luxury was much more based on who you are, but now it is definitely about what you have done. Brands are looking for people with results, across industries, people that have proven themselves as key collaborators, innovators, people that can manage change.”
She further adds:
“We are noticing luxury brands really looking into other industries for both talent and inspiration. When you talk about digital, brands are looking to Google or pure play companies. In retail they are looking to hospitality for knowledge of customer service. Luxury fashion brands are also speaking about Apple when it comes to best in class service and customer engagement.”

In the final analysis
In large corporations, the Boards should be held more accountable by paying closer attention to the behavior and actions in the C-suite ‒ thus reacting before things go awry.
The top executive’s job is to operate a business that adds value by means of the goods and services it provides to customers.
The way to solve an organizational problem is to confront the structural issues with a moral sense of purpose and ethics. Higher morale generates higher profits – though occasionally other priorities undermine that objective, for example, self-serving behavior by certain executives or chasing short-term selfish objectives in search of rapid market share, profits and self-interests before people. Monsanto’s executive conduct would make for a marvelous case study in this regard.
According to marketing maven Seth Godin, “It’s the flameouts and the scams that get all the publicity, but it’s the long-term commitment that pays off.”
In the end, what you manage and how you manage it is what you get.












______________________________________
Request your TWO FREE chapters of this popular book with no obligation.

Learn how to start or expand a business for free at

Google