In today’s competitive business landscape, having a talented and dedicated workforce is no longer just a nice-to-have; it’s an essential component of growth, innovation, and long-term sustainability. Top talent can drive your business forward, foster a culture of excellence, and provide a competitive edge that sets you apart from your rivals. However, attracting and retaining top talent is easier said than done. With the job market becoming increasingly competitive and employees seeking more than just a paycheck, businesses must adopt a strategic and holistic approach to talent management. In this episode, we’ll explore proven strategies and best practices for seeking, hiring, and retaining top talent, ensuring that your organization remains a magnet for the best and brightest minds in your industry.
The Importance of Top Talent
Before I delve into the strategies, let’s first understand why top talent is so crucial for business success:
- Increased Productivity and Efficiency: Top talent is often more skilled, motivated, and efficient, leading to higher productivity and better utilization of resources.
- Innovation and Creativity: Talented individuals bring fresh perspectives, innovative ideas, and creative solutions to the table, driving your business forward and keeping you ahead of the competition.
- Improved Customer Satisfaction: Top talent is better equipped to understand and meet the needs of your customers, leading to improved customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Competitive Advantage: In today’s knowledge-based economy, having a talented workforce can be a significant competitive advantage, setting your business apart from others in your industry.
- Positive Company Culture: Top talent often contributes to a positive and dynamic company culture, fostering an environment of continuous learning, growth, and collaboration.
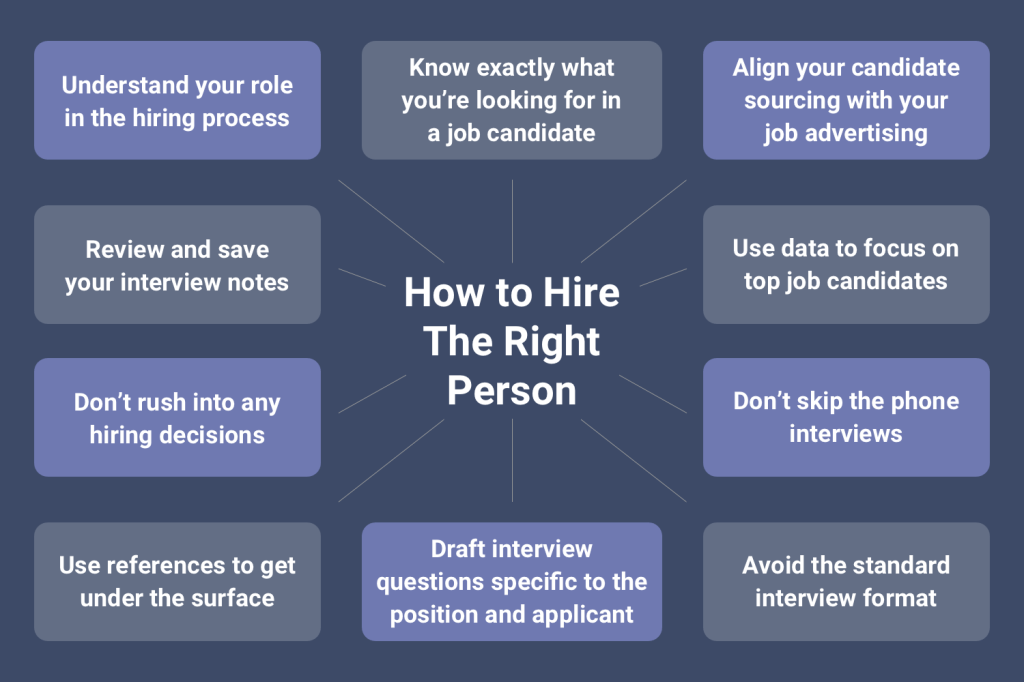
Strategies for Seeking and Hiring Top Talent
Now that we understand the importance of top talent, let’s explore some strategies for seeking and hiring the best candidates:
- Define Your Ideal Candidate: Before you start the hiring process, clearly define the skills, qualifications, and attributes you’re looking for in an ideal candidate. This will help you streamline your search and attract the right talent.
- Leverage Your Network: Tap into your professional network, industry associations, and employee referral programs to identify potential candidates. Word-of-mouth and personal recommendations can be invaluable in finding top talent.
- Optimize Your Job Postings: Craft compelling job postings that accurately reflect the role, responsibilities, and company culture. Use language that resonates with top talent and highlights the unique value proposition of your organization.
- Implement Structured Interviews: Develop a structured interview process, preferably with the hiring manager, that allows you to assess candidates’ skills, experience, and cultural fit objectively. Involve other stakeholders to gain diverse perspectives.
- Offer Competitive Compensation and Benefits: Top talent often commands higher salaries and better benefits. Be prepared to offer competitive compensation packages that align with industry standards and reflect the value you place on top talent.
Strategies for Retaining Top Talent
Hiring top talent is just the first step; retaining them is equally important. Here are some strategies to help you keep your best employees engaged and motivated:
- Foster a Positive Company Culture: Cultivate a positive and inclusive company culture that values diversity, collaboration, and continuous learning. Encourage open communication and create opportunities for personal and professional growth.
- Provide Opportunities for Growth and Development: Invest in the growth and development of your employees by offering training programs, mentorship opportunities, and clear career paths. Top talent thrives when they can continuously learn and advance.
- Recognize and Reward Excellence: Implement a robust recognition and reward system that acknowledges and celebrates the achievements and contributions of your top performers. This can include bonuses, promotions, or public acknowledgment.
- Offer Flexibility and Work-Life Balance: Top talent often values flexibility and work-life balance. Consider offering flexible work arrangements, remote work options, and generous time-off policies to accommodate their personal and professional needs.
- Encourage Autonomy and Ownership: Empower your top talent by giving them autonomy and ownership over their work. Allow them to take calculated risks, make decisions, and contribute to the overall direction of the organization.
- Provide Competitive Compensation and Benefits: Regularly review and adjust your compensation and benefits packages to ensure they remain competitive and aligned with industry standards. Top talent is often sought after, and you want to avoid losing them to competitors offering better packages.
In Conclusion
Attracting and retaining top talent is a critical component of business success in today’s competitive landscape. By implementing the strategies outlined in this episode, you can position your organization as a magnet for the best and brightest minds in your industry. Remember, talent management is an ongoing process that requires dedication, commitment, and a genuine appreciation for the value that top talent brings to your organization. Invest in your people, foster a positive and inclusive culture, and provide opportunities for growth and development, and you’ll be well on your way to building a talented and dedicated workforce that drives your business forward.
__________________________________________________________
Visit my business SAVVYPRENEURSHIP channel and if you like the content, kindly subscribe to help me grow the channel.
https://www.youtube.com/@Savvypreneurship